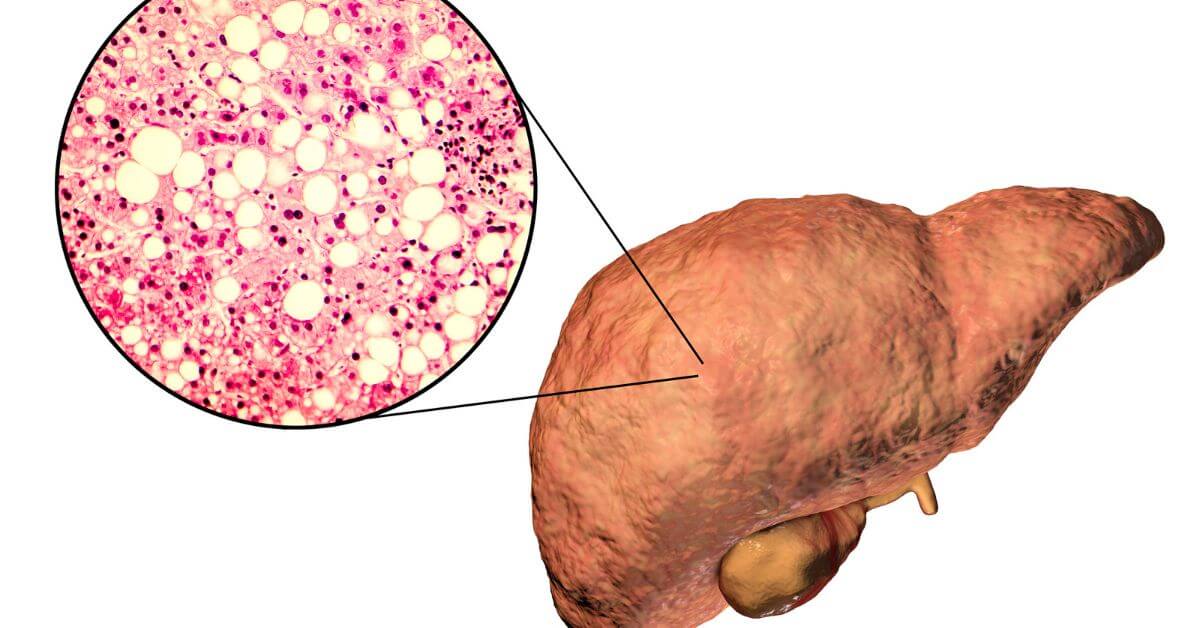
A Fatty liver, which is characterized by excessive fat accumulation in the liver, can result in liver failure. However, you can effectively manage fatty liver through a healthful eating approach. By focusing on specific foods and avoiding others here we give to make it an approachable fatty liver diet plan where you can start treating and preventing further progression of this condition.
Discover the comprehensive and actionable diet plan for fatty liver disease.
What is NAFLD??
NAFLD can progress to cirrhosis and liver failure If left untreated. Unlike alcohol-related liver disease, NAFLD is not caused by heavy alcohol consumption and is more commonly found in individuals with conditions such as obesity and type 2 diabetes.
The liver plays a crucial role in removing toxins and producing bile, which helps break down fats for digestion. Fatty liver disease disrupts the liver’s normal functioning, but lifestyle changes can prevent its progression.
The primary approach to treating NAFLD is weight loss, achieved through a combination of calorie reduction, regular exercise, and a healthy eating plan.
The Fatty Liver Diet Plan includes the following principles:
1. Fruits and Vegetables:
– Include a variety of fruits and vegetables in your diet, as they are rich in nutrients and fiber, which promote liver health.
2. High-Fiber Plants:
– Consume legumes and whole grains, which are high in fiber. They not only support liver health but also improve gut health.
3. Reduced Intake of Certain Foods and Beverages:
– Significantly limit foods high in added sugar, salt, refined carbohydrates, and saturated fat, as they contribute to weight gain and increase blood sugar levels.
4. No Alcohol:
– Completely avoid alcohol consumption, as it can exacerbate fatty liver disease and damage the liver.
To effectively treat NAFLD, the amount of weight loss required depends on the extent of excess body fat. Your healthcare team can help determine a suitable weight loss goal based on your overall health. Generally, a nutrient-dense, whole-food-based diet that includes fiber, protein, and unsaturated fats is recommended for individuals with NAFLD.
Which Specific Foods Can Be Included in a Healthy Liver Diet?
1. Coffee:
– Regular coffee consumption has been associated with a reduced risk of developing NAFLD. It may also lower abnormal liver enzyme levels.
2. Greens:
– Leafy greens like spinach contain compounds that can help combat fatty liver disease. Raw spinach, in particular, has shown promising results in lowering the risk of NAFLD.
3. Beans and Soy:
– Legumes such as lentils, chickpeas, and soybeans are not only nutritionally dense but also contain resistant starches that promote gut health.
4. Fatty Fish:
– Fatty fish like salmon, sardines, tuna, and trout are rich in omega-3 fatty acids.
5. Oatmeal:
– Whole-grain, fiber-rich foods like oatmeal are associated with a reduced risk of NAFLD-related diseases.
6. Nuts:
– A diet rich in nuts has been linked to reduced inflammation, insulin resistance, oxidative stress, and a lower prevalence of NAFLD.
7. Turmeric:
– Curcumin, the active compound in turmeric, may reduce markers of liver damage in people with NAFLD. Turmeric supplementation has been found to decrease levels of certain liver enzymes.
8. Sunflower Seeds:
– Sunflower seeds are high in vitamin E, an antioxidant used in the treatment of NAFLD. Increasing vitamin E consumption naturally through foods like sunflower seeds can be beneficial.
9. Unsaturated Fats:
– Replace sources of saturated fat, such as butter and fatty meats, with healthier options like avocados, olive oil, nut butter, and fatty fish. The Mediterranean diet, which emphasizes unsaturated fats, is often recommended for individuals with NAFLD.
10. Garlic:
– Garlic powder supplements and raw garlic consumption have shown potential in reducing body weight, liver fat, and liver enzyme levels in people with fatty liver disease.
It is important to avoid certain items that can worsen fatty liver disease:
- – Alcohol: Abstain from alcohol completely, as it can cause further liver damage.
- – Added Sugar: Stay away from sugary foods and beverages, which contribute to weight gain and liver fat buildup.
- – Fried Foods: High in fat and calories, fried foods should be limited or avoided.
- – Added Salt: Limit sodium intake to reduce the risk of NAFLD and related conditions.
- – White Bread, Rice, and Pasta: Opt for whole grains over refined carbohydrates, as they provide more fiber and have a lower impact on blood sugar levels.
- – Red Meat: High in saturated fat, red meat should be consumed in moderation or replaced with leaner protein sources.
Other Lifestyle Changes
Remember, along with modifying your diet, there are other lifestyle changes you can make to improve your liver health:
- – Regular Exercise: Engage in aerobic exercise for at least 30 minutes most days of the week to manage weight and liver disease.
- – Lower Blood Lipid Levels: Watch your saturated fat and sugar intake to control cholesterol and triglyceride levels. Medication may be necessary in some cases.
- – Control Diabetes: Manage both diabetes and fatty liver disease through diet, exercise, and medications if needed.
Questions & Answers
1. Q: What is a fatty liver diet plan?
A: A fatty liver diet plan is a specialized eating approach designed to support the management and improvement of fatty liver disease. The diet aims to promote weight loss, reduce inflammation, and improve overall liver health.
2. Q: What foods should I include in a fatty liver diet plan?
A: In a fatty liver diet plan, it is important to include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, lean proteins (such as poultry, fish, and tofu), and healthy fats (like avocados, nuts, and olive oil). These foods provide essential nutrients, fiber, and antioxidants that support liver health and help manage fatty liver disease.
3. Q: Are there any foods I should avoid in a fatty liver diet plan?
A: Yes, there are certain foods you should limit or avoid in a fatty liver diet plan. These include alcohol, added sugars (found in sugary beverages, desserts, and processed foods), fried foods, foods high in salt, refined carbohydrates (like white bread and pasta), and red meats. These foods can contribute to weight gain, liver fat accumulation, and increased inflammation, which can worsen fatty liver disease.
4. Q: How can exercise complement a fatty liver diet plan?
A: Exercise plays a crucial role in managing fatty liver disease and can complement a diet plan. Regular physical activity, such as aerobic exercises (walking, jogging, cycling), can help promote weight loss, improve insulin sensitivity, reduce liver fat, and enhance overall liver function. It is recommended to engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous exercise per week, along with strength training exercises.
5. Q: Can a fatty liver diet plan help reverse fatty liver disease?
A: Yes, a fatty liver diet plan, combined with lifestyle modifications like regular exercise and weight loss, can help reverse fatty liver disease in many cases. By adopting a healthy eating pattern, reducing fat accumulation in the liver, and promoting weight loss, individuals may experience improvements in liver function, reduced inflammation, and a decrease in liver fat content. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized guidance and to monitor progress.
Remember, the answers provided are general in nature, and it is always recommended to seek personalized advice from healthcare professionals or registered dietitians who can provide tailored guidance based on individual health conditions and needs.